Page 18 - ISQ Outlook 2023
P. 18
INVESTMENT STRATEGY QUARTERLY
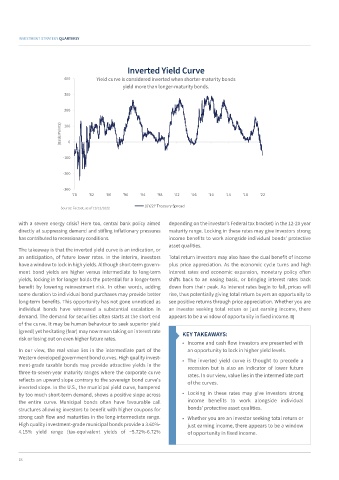
Inverted Yield Curve
400 Yield curve is considered inverted when shorter-maturity bonds
yield more than longer-maturity bonds.
300
200
(Basis Points) 100 0
-100
-200
-300
'78 '82 '86 '90 '94 '98 '02 '06 '10 '14 '18 '22
Source: Factset, as of 19/12/2022 10Y/2Y Treasury Spread
with a severe energy crisis? Here too, central bank policy aimed depending on the investor’s Federal tax bracket) in the 12-20 year
directly at suppressing demand and stifling inflationary pressures maturity range. Locking in these rates may give investors strong
has contributed to recessionary conditions. income benefits to work alongside individual bonds’ protective
asset qualities.
The takeaway is that the inverted yield curve is an indication, or
an anticipation, of future lower rates. In the interim, investors Total return investors may also have the dual benefit of income
have a window to lock in high yields. Although short-term govern- plus price appreciation. As the economic cycle turns and high
ment bond yields are higher versus intermediate to long-term interest rates end economic expansion, monetary policy often
yields, locking in for longer holds the potential for a longer-term shifts back to an easing basis, or bringing interest rates back
benefit by lowering reinvestment risk. In other words, adding down from their peak. As interest rates begin to fall, prices will
some duration to individual bond purchases may provide better rise, thus potentially giving total return buyers an opportunity to
long-term benefits. This opportunity has not gone unnoticed as see positive returns through price appreciation. Whether you are
individual bonds have witnessed a substantial escalation in an investor seeking total return or just earning income, there
demand. The demand for securities often starts at the short end appears to be a window of opportunity in fixed income.
of the curve. It may be human behaviour to seek superior yield
(greed) yet hesitating (fear) may now mean taking on interest rate KEY TAKEAWAYS:
risk or losing out on even higher future rates.
• Income and cash flow investors are presented with
In our view, the real value lies in the intermediate part of the an opportunity to lock in higher yield levels.
Western developed government bond curves. High quality invest- • The inverted yield curve is thought to precede a
ment-grade taxable bonds may provide attractive yields in the recession but is also an indicator of lower future
three-to-seven-year maturity ranges where the corporate curve rates. In our view, value lies in the intermediate part
reflects an upward slope contrary to the sovereign bond curve's of the curves.
inverted slope. In the U.S., the municipal yield curve, hampered
by too much short-term demand, shows a positive slope across • Locking in these rates may give investors strong
the entire curve. Municipal bonds often have favourable call income benefits to work alongside individual
structures allowing investors to benefit with higher coupons for bonds’ protective asset qualities.
strong cash flow and maturities in the long-intermediate range. • Whether you are an investor seeking total return or
High quality investment-grade municipal bonds provide a 3.60%- just earning income, there appears to be a window
4.15% yield range (tax-equivalent yields of ~5.72%-6.72% of opportunity in fixed income.
18