Page 17 - ISQ Outlook 2023
P. 17
INVESTMENT STRATEGY QUARTERLY
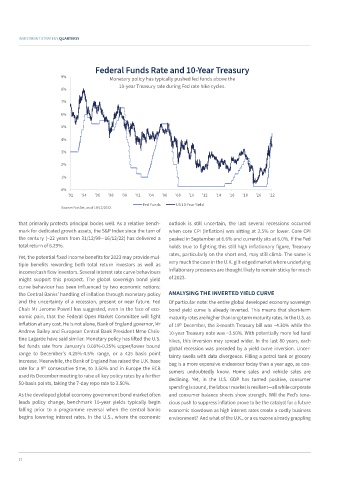
Federal Funds Rate and 10-Year Treasury
9% Monetary policy has typically pushed fed funds above the
10-year Treasury rate during Fed rate hike cycles.
8%
7%
6%
5%
4%
3%
2%
1%
0%
'92 '94 '96 '98 '00 '02 '04 '06 '08 '10 '12 '14 '16 '18 '20 '22
Fed Funds US 10-Year Yield
Source: FactSet, as of 19/12/2022.
that primarily protects principal bodes well. As a relative bench- outlook is still uncertain, the last several recessions occurred
mark for dedicated growth assets, the S&P Index since the turn of when core CPI (inflation) was sitting at 2.5% or lower. Core CPI
the century (~22 years from 31/12/99—16/12/22) has delivered a peaked in September at 6.6% and currently sits at 6.0%. If the Fed
total return of 6.29%. holds true to fighting this still high inflationary figure, Treasury
rates, particularly on the short end, may still climb. The same is
Yet, the potential fixed income benefits for 2023 may provide mul-
tiple benefits rewarding both total return investors as well as very much the case in the U.K. gilt-edged market where underlying
income/cash flow investors. Several interest rate curve behaviours inflationary pressures are thought likely to remain sticky for much
might support this prospect. The global sovereign bond yield of 2023.
curve behaviour has been influenced by two economic notions:
the Central Banks' handling of inflation through monetary policy ANALYSING THE INVERTED YIELD CURVE
and the uncertainty of a recession, present or near future. Fed Of particular note: the entire global developed economy sovereign
Chair Mr Jerome Powell has suggested, even in the face of eco- bond yield curve is already inverted. This means that short-term
nomic pain, that the Federal Open Market Committee will fight maturity rates are higher than long-term maturity rates. In the U.S. as
inflation at any cost. He is not alone, Bank of England governor, Mr of 19 December, the 3-month Treasury bill was ~4.30% while the
th
Andrew Bailey and European Central Bank President Mme Chris- 10-year Treasury note was ~3.50%. With potentially more fed fund
tine Lagarde have said similar. Monetary policy has lifted the U.S. hikes, this inversion may spread wider. In the last 80 years, each
fed funds rate from January’s 0.00%-0.25% upper/lower bound global recession was preceded by a yield curve inversion. Uncer-
range to December’s 4.25%-4.5% range, or a 425 basis point tainty swells with data divergence. Filling a petrol tank or grocery
increase. Meanwhile, the Bank of England has raised the U.K. base bag is a more expensive endeavour today than a year ago, as con-
rate for a 9 consecutive time, to 3.50% and in Europe the ECB sumers undoubtedly know. Home sales and vehicle sales are
th
used its December meeting to raise all key policy rates by a further declining. Yet, in the U.S. GDP has turned positive, consumer
50-basis points, taking the 7-day repo rate to 3.50%.
spending is sound, the labour market is resilient—all while corporate
As the developed global economy government bond market often and consumer balance sheets show strength. Will the Fed’s tena-
leads policy change, benchmark 10-year yields typically begin cious push to suppress inflation prove to be the catalyst for a future
falling prior to a programme reversal when the central banks economic slowdown as high interest rates create a costly business
begins lowering interest rates. In the U.S., where the economic environment? And what of the U.K., or a eurozone already grappling
17