Page 7 - ISQ - April 2022
P. 7
INVESTMENT STRATEGY QUARTERLY
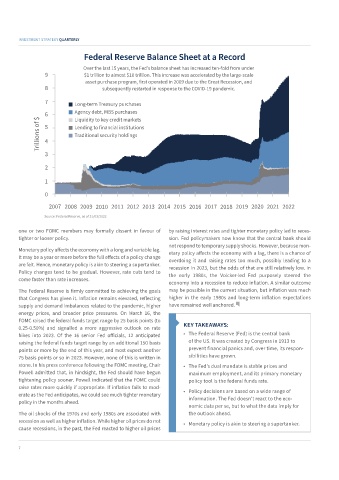
Federal Reserve Balance Sheet at a Record
Over the last 15 years, the Fed’s balance sheet has increased ten-fold from under
9 $1 trillion to almost $10 trillion. This increase was accelerated by the large-scale
asset purchase program, first operated in 2009 due to the Great Recession, and
8 subsequently restarted in response to the COVID-19 pandemic.
7 Long-term Treasury purchases
Agency debt, MBS purchases
Trillions of $ 6 Liquidity to key credit markets
5
Lending to financial institutions
Traditional security holdings
4
3
2
1
0
2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022
Source: Federal Reserve, as of 31/03/2022
one or two FOMC members may formally dissent in favour of by raising interest rates and tighter monetary policy led to reces-
tighter or looser policy. sion. Fed policymakers now know that the central bank should
not respond to temporary supply shocks. However, because mon-
Monetary policy affects the economy with a long and variable lag. etary policy affects the economy with a lag, there is a chance of
It may be a year or more before the full effects of a policy change overdoing it and raising rates too much, possibly leading to a
are felt. Hence, monetary policy is akin to steering a supertanker. recession in 2023, but the odds of that are still relatively low. In
Policy changes tend to be gradual. However, rate cuts tend to the early 1980s, the Volcker-led Fed purposely steered the
come faster than rate increases.
economy into a recession to reduce inflation. A similar outcome
The Federal Reserve is firmly committed to achieving the goals may be possible in the current situation, but inflation was much
that Congress has given it. Inflation remains elevated, reflecting higher in the early 1980s and long-term inflation expectations
supply and demand imbalances related to the pandemic, higher have remained well anchored.
energy prices, and broader price pressures. On March 16, the
FOMC raised the federal funds target range by 25 basis points (to
0.25-0.50%) and signalled a more aggressive outlook on rate KEY TAKEAWAYS:
hikes into 2023. Of the 16 senior Fed officials, 12 anticipated • The Federal Reserve (Fed) is the central bank
raising the federal funds target range by an additional 150 basis of the US. It was created by Congress in 1913 to
points or more by the end of this year, and most expect another prevent financial panics and, over time, its respon-
75 basis points or so in 2023. However, none of this is written in sibilities have grown.
stone. In his press conference following the FOMC meeting, Chair • The Fed’s dual mandate is stable prices and
Powell admitted that, in hindsight, the Fed should have begun maximum employment, and its primary monetary
tightening policy sooner. Powell indicated that the FOMC could policy tool is the federal funds rate.
raise rates more quickly if appropriate. If inflation fails to mod-
erate as the Fed anticipates, we could see much tighter monetary • Policy decisions are based on a wide range of
policy in the months ahead. information. The Fed doesn’t react to the eco-
nomic data per se, but to what the data imply for
The oil shocks of the 1970s and early 1980s are associated with the outlook ahead.
recession as well as higher inflation. While higher oil prices do not • Monetary policy is akin to steering a supertanker.
cause recessions, in the past, the Fed reacted to higher oil prices
7